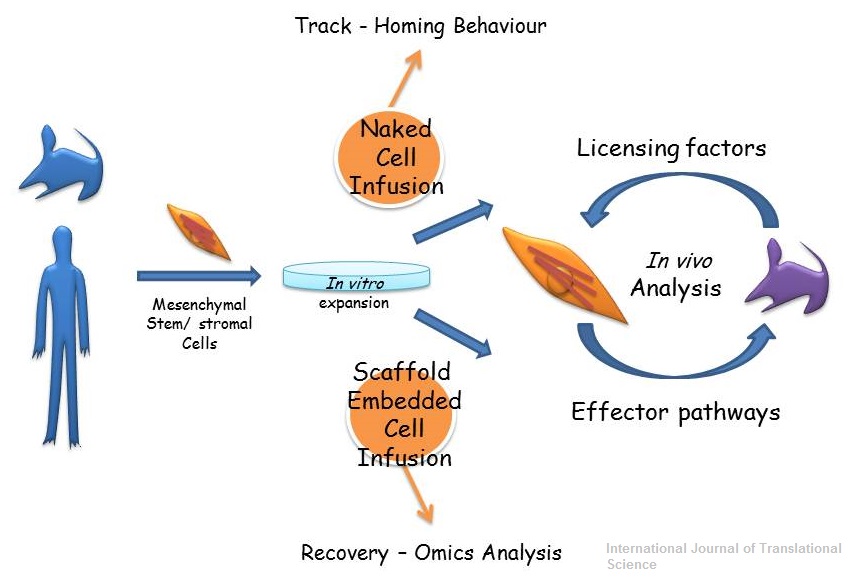
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells are effective therapeutic agents for a variety
of pathological conditions. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying
their action remain largely unknown and biased by in vitro studies. In this
concise review we have described recent advances in MSC therapeutics based
on in vivo observations. We have also discussed the possibility of using
engineering approaches to improve and facilitate deciphering MSC functions
References
Therapeutic Immunomodulation with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells 31
F. J. Lv, R. S. Tuan, K. M. Cheung, and V. Y. Leung. “Concise review: the
surface markers and identity of human mesenchymal stem cells.” Stem
Cells 32, 1408–1419. (2014).
M. Maleki, F. Ghanbarvand, M. Reza Behvarz, M. Ejtemaei, and
E. Ghadirkhomi. “Comparison of mesenchymal stem cell markers in
multiple human adult stem cells.” Int. J. Stem Cells 7, 118–126.
(2014).
R. Hass, C. Kasper, S. B ̈ohm, and R. Jacobs. “Different populations
and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): A comparison
of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC.” Cell Commun. Signal 9,
(2011).
A. Shaer, N. Azarpira, M. H. Aghdaie, and E. Esfandiari. “Isolation and
characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived from
Placental Decidua Basalis; Umbilical cord Wharton’s Jelly and Amniotic
Membrane.” Pak. J. Med. Sci. 30, 1022–1026. (2014).
E. Collins, F. Gu, M. Qi, I. Molano, P. Ruiz, L. Sun, et al. “Differential
efficacy of human mesenchymal stem cells based on source of origin,”
J. Immunol. 193, 4381–4390. (2014).
W. Liu, F. Song, L. Ren, W. Guo, T. Wang, Y. Feng, et al. “The multiple
functional roles of mesenchymal stem cells in participating in treating
liver diseases.” J. Cell Mol. Med. (2014).
M. J. Goumans, J. A. Maring, and A. M. Smits. “A straightforward guide
to the basic science behind cardiovascular cell-based therapies.” Heart
, 1153–1157. (2014).
J. Bashir, A. Sherman, H. Lee, L. Kaplan, and J. M. Hare. “Mesenchymal
stem cell therapies in the treatment of musculoskeletal diseases.” PMR
, 61–69. (2014).
M. Baghaban Eslaminejad and E. Malakooty Poor. “Mesenchymal stem
cells as a potent cell source for articular cartilage regeneration,” World
J. Stem Cells 6, 344–354. (2014).
B. Kristj ́ansson and S. Honsawek. “Current perspectives in mesenchymal
stem cell therapies for osteoarthritis.” Stem Cells Int. 2014, 194318.
(2014).
J. F. Swart and N. M. Wulffraat. “Mesenchymal stromal cells for
treatment of arthritis.” Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 28, 589–603.
(2014).
Y. Liu, J. Wu, Y. Zhu, and J. Han. “Therapeutic application of mesenchy-
mal stem cells in bone and joint diseases,” Clin. Exp. Med. 4, 13–24.
(2014).
L. Dolcetti and F. Dazzi
B. Skovrlj, G. Cunn, J. Guzman, and S. A. Qureshi. “Mesenchymal
stem cell technology in the treatment of degenerative disc disease.”
J. Neurosurg. Sci. (2014).
M. Boido, A. Piras, V. Valsecchi, G. Spigolon, K. Mareschi, I. Ferrero,
et al. “Human mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation modulates
neuroinflammatory milieu in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis.” Cytotherapy 16, 1059–1072. (2014).
L. Mazzini, K. Mareschi, I. Ferrero, M. Miglioretti, A. Stecco, S. Servo,
et al. “Mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation in amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis: a long-term safety study.” Cytotherapy 14, 56–60. (2012).
K. A. Chang, H. J. Kim, Y. Joo, S. Ha, and Y. H. Suh. “The therapeutic
effects of human adipose-derived stem cells in Alzheimer’s disease
mouse models.” Neurodegener. Dis. 13, 99–102. (2014).
N. Kim and S. G. Cho. “Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells.”
Korean J. Int. Med. 28, 387–402. (2013).
E. Buzhor, L. Leshansky, J. Blumenthal, H. Barash, D. Warshawsky,
Y. Mazor, et al. “Cell-based therapy approaches: the hope for incurable
diseases.” Regen Med. 9, 649–672. (2014).
K. Le Blanc, F. Frassoni, L. Ball, F. Locatelli, H. Roelofs, I. Lewis,
et al. “Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant,
severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study.” Lancet 371,
–1586. (2008).
J. Tan, W. Wu, X. Xu, L. Liao, F. Zheng, S. Messinger, et al. “Induction
therapy with autologous mesenchymal stem cells in living-related kidney
transplants: a randomized controlled trial.” JAMA 307, 1169–77. (2012).
R. Ciccocioppo, M. E. Bernardo, A. Sgarella, R. Maccario, M. A.
Avanzini, C. Ubezio, et al. “Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchy-
mal stromal cells in the treatment of fistulising Crohn’s disease.” Gut 60,
–798. (2011).
P. Connick, M. Kolappan, C. Crawley, D. J. Webber, R. Patani, A. W.
Michell, et al. “Autologous mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of
secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: an open-label phase 2a proof-
of-concept study.” Lancet Neurol. 11, 150–156. (2012).
I. M ̈uller, S. Lymperi, and F. Dazzi. “Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for
degenerative inflammatory disorders.” Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant.
, 639–644. (2008).
D. Polchert, J. Sobinsky, G. Douglas, M. Kidd, A. Moadsiri, E. Reina,
et al. “IFN-gamma activation of mesenchymal stem cells for treatment
Therapeutic Immunomodulation with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells 33
and prevention of graft versus host disease.” Eur. J. Immunol. 38,
–1755. (2008).
G. Ren, L. Zhang, X. Zhao, G. Xu, Y. Zhang, A. I. Roberts, et al. “Mes-
enchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted
action of chemokines and nitric oxide.” Cell Stem Cell 2, 141–150.
(2008).
M. Krampera. “Mesenchymal stromal cell ‘licensing’: a multistep
process.” Leukemia 25, 1408–1414. (2011).
L. Wang, Y. Zhao, and S. Shi. “Interplay between mesenchymal stem
cells and lymphocytes: implications for immunotherapy and tissue
regeneration.” J. Dent. Res. 91, 1003–1010. (2012).
I. Marigo and F. Dazzi. “The immunomodulatory properties of mes-
enchymal stem cells.” Semin. Immunopathol. 33, 593–602. (2011).
P. Renner, E. Eggenhofer, A. Rosenauer, F. C. Popp, J. F. Stein-
mann, P. Slowik, et al. “Mesenchymal stem cells require a sufficient,
ongoing immune response to exert their immunosuppressive function.”
Transplant Proc. 41, 2607–2611. (2009).
E. Valencic, C. Loganes, S. Cesana, E. Piscianz, G. Gaipa, E. Biagi, et al.
“Inhibition of mesenchymal stromal cells by pre-activated lymphocytes
and their culture media.” Stem Cell Res. Ther. 5, 3. (2014).
J. Su, X. Chen, Y. Huang, W. Li, J. Li, K. Cao, et al. “Phylogenetic
distinction of iNOS and IDO function in mesenchymal stem cell-
mediated immunosuppression in mammalian species.” Cell Death Differ.
, 388–396. (2014).
G. Ren, J. Su, L. Zhang, X. Zhao, W. Ling, A. L’huillie, et al. “Species
variation in the mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-mediated
immunosuppression.” Stem Cells 27, 1954–1962. (2009).
R. Meisel, S. Brockers, K. Heseler, O. Degistirici, H. B ̈ulle, C. Woite,
et al. “Human but not murine multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells
exhibit broad-spectrum antimicrobial effector function mediated by
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.” Leukemia 25, 648–654. (2011).
K. Schroder, K. M. Irvine, M. S. Taylor, N. J. Bokil, K. A. Le Cao,
K. A. Masterman, et al. “Conservation and divergence in Toll-like
receptor 4-regulated gene expression in primary human versus mouse
macrophages.” Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 109, E944–E953. (2012).
M. Orciani, A. Campanati, E. Salvolini, G. Lucarini, G. Di Benedetto,
A. Offidani, et al. “The mesenchymal stem cell profile in psoriasis.”
Br. J. Dermatol. 165, 585–592. (2011).
L. Dolcetti and F. Dazzi
H. J. Ball, F. F. Jusof, S. M. Bakmiwewa, N. H. Hunt, and H. J. Yuasa.
“Tryptophan-catabolizing enzymes - party of three.” Front. Immunol.
:485. (2014).
K. English, F. P. Barry, C. P. Field-Corbett, and B. P. Mahon.
“IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha differentially regulate immunomodula-
tion by murine mesenchymal stem cells.” Immunol. Lett. 110, 91–100.
(2007).
H. Y. Jui, C. H. Lin, W. T. Hsu, Y. R. Liu, R. B. Hsu, B. L. Chiang,
et al. “Autologous mesenchymal stem cells prevent transplant arterio-
sclerosis by enhancing local expression of interleukin-10, interferon-γ,
and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.” Cell Transplant 21, 971–984. (2012).
W. Ge, J. Jiang, J. Arp, W. Liu, B. Garcia, and H. Wang. “Regulatory
T-cell generation and kidney allograft tolerance induced by mesenchymal
stem cells associated with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression.”
Transplantation 90, 1312–1320. (2010).
D. Wang, X. Feng, L. Lu, J. E. Konkel, H. Zhang, Z. Chen, et al. “A CD8
T cell/indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase axis is required for mesenchymal
stem cell suppression of human systemic lupus erythematosus.” Arthritis
Rheumatol. 66, 2234–2245. (2014).
D. Chabannes, M. Hill, E. Merieau, J. Rossignol, R. Brion, J. P. Soulillou,
et al. “A role for heme oxygenase-1 in the immunosuppressive effect of
adult rat and human mesenchymal stem cells.” Blood 110, 3691–3694.
(2007).
C. Bouffi, C. Bony, G. Courties, C. Jorgensen, and D. No ̈el. “IL-6-
dependent PGE2 secretion by mesenchymal stem cells inhibits local
inflammation in experimental arthritis,” PLoS ONE 5:e14247. (2010).
L. Zhang, R. J. Dang, H. Li, P. Li, Y. M. Yang, X. M. Guo, et al. “SOCS1
regulates the immune modulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells
by inhibiting nitric oxide production.” PLoS ONE 9:e97256. (2014).
Y. Huang, P. Yu, W. Li, G. Ren, A. I. Roberts, W. Cao, et al. “p53
regulates mesenchymal stem cell-mediated tumor suppression in a
tumor microenvironment through immune modulation.” Oncogene 33,
–3838. (2014).
D. Claar, T. V. Hartert, and R. S. Peebles. “The role of prostaglandins
in allergic lung inflammation and asthma.” Expert Rev. Respir Med.
–18. (2014).
K. Kawahara, H. Hohjoh, T. Inazumi, S. Tsuchiya, and Y. Sugimoto.
“Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: Relevance of prostaglandin E
receptors.” Biochim. Biophys. Acta (2014).
Therapeutic Immunomodulation with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells 35
P. Kalinski. “Regulation of immune responses by prostaglandin E2.”
J. Immunol. 188, 21–28. (2012).
Y. C. Wang, S. H. Wang, Y. N. Wei, D. W. Du, H. Xu, C. C. Gao, et al.
“Notch-RBP-J signaling is required by bone marrow stromal cells for the
treatment of acute graft versus host disease.” Stem Cell Res. 11, 721–735.
(2013).
T. J. Bartosh, J. H. Yl ̈ostalo, N. Bazhanov, J. Kuhlman, and D. J. Prockop.
“Dynamic compaction of human mesenchymal stem/precursor cells
into spheres self-activates caspase-dependent IL1 signaling to enhance
secretion of modulators of inflammation and immunity (PGE2, TSG6,
and STC1).” Stem Cells 31, 2443–2456. (2013).
Y. Qiu, M. M. Yun, X. Han, R. Zhao, E. Zhou, and S. Yun. “Human umbili-
cal cord mesenchymal stromal cells suppress MHC class II expression on
rat vascular endothelium and prolong survival time of cardiac allograft.”
Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 7, 1760–1767. (2014).
M. Koch, A. Lehnhardt, X. Hu, B. Brunswig-Spickenheier, M. Stolk,
V. Br ̈ocker, et al. “Isogeneic MSC application in a rat model of acute
renal allograft rejection modulates immune response but does not prolong
allograft survival.” Transpl. Immunol. 29, 43–50. (2013).
R. A. Larocca, P. M. Moraes-Vieira, E. J. Bassi, P. Semedo, D. C. de
Almeida, M. B. da Silva, et al. “Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal
stem cells increase skin allograft survival and inhibit Th-17 immune
response.” PLoS ONE 8:e76396. (2013).
M. A. Gonz ́alez, E. Gonzalez-Rey, L. Rico, D. B ̈uscher, and M.
Delgado. “Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experi-
mental colitis by inhibiting inflammatory and autoimmune responses.”
Gastroenterology 136, 978–989. (2009).
E. Gonzalez-Rey, P. Anderson, M. A. Gonz ́alez, L. Rico, D. B ̈uscher,
and M. Delgado. “Human adult stem cells derived from adipose tis-
sue protect against experimental colitis and sepsis.” Gut 58, 929–939.
(2009).
Q. Q. Chen, L. Yan, C. Z. Wang, W. H. Wang, H. Shi, B. B. Su, et al.
“Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate TNBS-induced colitis by modulating
inflammatory and autoimmune responses.” World J. Gastroenterol. 19,
–4717. (2013).
H. Li, Z. Guo, H. Zhu, X. S. Li, X. Jiang, H. Yao, et al. “Trans-
planted mesenchymal stem cells can inhibit the three developmental
stages of murine acute graft-versus-host disease.” In Vivo 24, 659–666.
(2010).
L. Dolcetti and F. Dazzi
S. Chiesa, S. Morbelli, S. Morando, M. Massollo, C. Marini, A. Bertoni,
et al. “Mesenchymal stem cells impair in vivo T-cell priming by dendritic
cells.” Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 108, 17384–1739. (2011).
H. Li, Z. Guo, X. Jiang, H. Zhu, X. Li, and N. Mao. “Mesenchymal
stem cells alter migratory property of T and dendritic cells to delay the
development of murine lethal acute graft-versus-host disease.” Stem Cells
, 2531–2541. (2008).
M. G. Kim, S. H. Kim, H. Noh, Y. S. Ko, H. Y. Lee, S. K. Jo, et al.
“CD11c+ cells partially mediate the renoprotective effect induced by
bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.” PLoS ONE 8:e72544.
(2013).
Y. Geng, L. Zhang, B. Fu, J. Zhang, Q. Hong, J. Hu, et al. “Mesenchymal
stem cells ameliorate rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury via
the activation of M2 macrophages.” Stem Cell Res. Ther. 5, 80. (2014).
D. I. Cho, M. R. Kim, H. Y. Jeong, H. C. Jeong, M. H. Jeong, S. H. Yoon,
et al. “Mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate the M1/M2 balance
in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages.” Exp. Mol. Med. 46:e70.
(2014).
B. L. Yen, M. L. Yen, P. J. Hsu, K. J. Liu, C. J. Wang, C. H. Bai,
et al. “Multipotent human mesenchymal stromal cells mediate expansion
of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via hepatocyte growth factor/c-met
and STAT3.” Stem Cell Rep. 1, 139–151. (2013).
H. W. Chen, H. Y. Chen, L. T. Wang, F. H. Wang, L. W. Fang, H. Y. Lai,
et al. “Mesenchymal stem cells tune the development of monocyte-
derived dendritic cells toward a myeloid-derived suppressive phenotype
through growth-regulated oncogene chemokines.” J. Immunol. 190,
–5077. (2013).
X. Su, L. Zhang, J. Ye, L. Yang, Y. Li, and Y. Wang. “Bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells suppress ascitogenous hepatoma progression
in BALB/c mouse through reducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells.”
Biomed. Mater Eng. 25, 167–177. (2015).
L. Senseb ́e and S. Fleury-Cappellesso. “Biodistribution of mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells in a preclinical setting.” Stem Cells Int. 2013, 678063.
(2013).
H. S. Kim, J. Woo, Y. Choi, E. H. Hwang, S. K. Choi, K. W. Cho, et al.
“Noninvasive MRI and multilineage differentiation capability of ferritin-
transduced human mesenchymal stem cells.” NMR Biomed (2014).
K. Geng, Z. X. Yang, D. Huang, M. Yi, Y. Jia, G. Yan, et al. “Tracking
of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with gadolinium diethylenetriamine
Therapeutic Immunomodulation with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells 37
pentaacetic acid by 7T magnetic resonance imaging in a model of
cerebral ischemia.” Mol. Med. Rep. 11, 954–960. (2015).
P. Hua, Y. Y. Wang, L. B. Liu, J. L. Liu, J. Y. Liu, Y. Q. Yang, et al. “In vivo
magnetic resonance imaging tracking of transplanted superparamagnetic
iron oxidelabeled bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats with
myocardial infarction.” Mol. Med. Rep. 11, 113–1120. (2015).
Jasmin, L. A. Jelicks, H. B. Tanowitz, V. M. Peters, R. Mendez-Otero,
A. C. Campos de Carvalho, et al. “Molecular imaging, biodistribution
and efficacy of mesenchymal bone marrow cell therapy in a mouse model
of Chagas disease.” Microbes Infect 16, 923–935. (2014).
A. Gholamrezanezhad, S. Mirpour, M. Bagheri, M. Mohamadnejad, K.
Alimoghaddam, L. Abdolahzadeh, et al. “In vivo tracking of 111In-
oxine labeled mesenchymal stem cells following infusion in patients
with advanced cirrhosis.” Nucl. Med. Biol. 38, 961–917. (2011).
O. Betzer, A. Shwartz, M. Motiei, G. Kazimirsky, I. Gispan, E. Damti,
et al. “Nanoparticle-based CT imaging technique for longitudinal and
quantitative stem cell tracking within the brain: application in neuropsy-
chiatric disorders.” ACS Nano 8, 9274–9285. (2014).
E. Wolfs, T. Struys, T. Notelaers, S. J. Roberts, A. Sohni, G. Bormans,
et al. ”18F-FDG labeling of mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent
adult progenitor cells for PET imaging: effects on ultrastructure and
differentiation capacity.” J. Nucl. Med. 54, 447–454. (2013).
M. Kantarcioglu, B. Caliskan, H. Demirci, O. Karacalioglu, M. Kekilli,
Z. Polat, et al. “The efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in
caustic esophagus injury: an experimental study.” Stem Cells Int. 2014,
(2014).
M. Hofmann, K. C. Wollert, G. P. Meyer, A. Menke, L. Arseniev, B.
Hertenstein, et al. “Monitoring of bone marrow cell homing into the
infarcted human myocardium.” Circulation 111, 2198–2202. (2005).
T. Garg, O. Singh, S. Arora, and R. Murthy. “Scaffold: a novel carrier
for cell and drug delivery.” Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 29, 1–63.
(2012).
A. Goren, N. Dahan, E. Goren, L. Baruch, and M. Machluf. “Encapsulated
human mesenchymal stem cells: a unique hypoimmunogenic platform
for long-term cellular therapy.” FASEB J. 24, 22–31. (2010).
J. F. Markusen, C. Mason, D. A. Hull, M. A. Town, A. B. Tabor, M.
Clements, et al. “Behavior of adult human mesenchymal stem cells
entrapped in alginate-GRGDY beads.” Tissue Eng. 12, 821–830. (2006).
L. Dolcetti and F. Dazzi
J. Barminko, J. H. Kim, S. Otsuka, A. Gray, R. Schloss, M. Grumet, et al.
“Encapsulated mesenchymal stromal cells for in vivo transplantation.”
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 108, 2747–2758. (2011).
L. Zanotti,A. Sarukhan, E. Dander, M. Castor, J. Cibella, C. Soldani, et al.
“Encapsulated mesenchymal stem cells for in vivo immunomodulation.”
Leukemia 27, 500–503. (2013).
R. P. Meier, R. Mahou, P. Morel, J. Meyer, E. Montanari, Y. D. Muller,
et al. “Microencapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells decrease liver
fibrosis in mice.” J. Hepatol. (2014).
X. Zhang, K. Yamaoka, K. Sonomoto, H. Kaneko, M. Satake,
Y. Yamamoto, et al. “Local delivery of mesenchymal stem cells with
poly-lactic-co-glycolic Acid nano-fiber scaffold suppress arthritis in
rats.” PLoS ONE 9:e114621. (2014).
S. J. Hwang, T. H. Cho, and I. S. Kim. “In vivo gene activity of human
mesenchymal stem cells after scaffold-mediated local transplantation.”
Tissue Eng Part A 20, 2350–2364. (2014).
C. H. Chen, H. J. Wei, W. W. Lin, I. Chiu, S. M. Hwang, C. C. Wang, et al.
“Porous tissue grafts sandwiched with multilayered mesenchymal stro-
mal cell sheets induce tissue regeneration for cardiac repair.” Cardiovasc
Res. 80, 88–95. (2008).
J. H. Brauker, V. E. Carr-Brendel, L. A. Martinson, J. Crudele, W. D.
Johnston, and R. C. Johnson. “Neovascularization of synthetic mem-
branes directed by membrane microarchitecture.” J. Biomed. Mater Res.
, 1517–1524. (1995).
T. A. Telemeco, C. Ayres, G. L. Bowlin, G. E. Wnek, E. D. Boland,
N. Cohen, et al. “Regulation of cellular infiltration into tissue engi-
neering scaffolds composed of submicron diameter fibrils produced by
electrospinning.” Acta Biomater. 1, 377–385. (2005).
B. J. Lawrence and S. V. Madihally. “Cell colonization in degradable 3D
porous matrices.” Cell Adh. Migr. 2, 9–16. (2008)