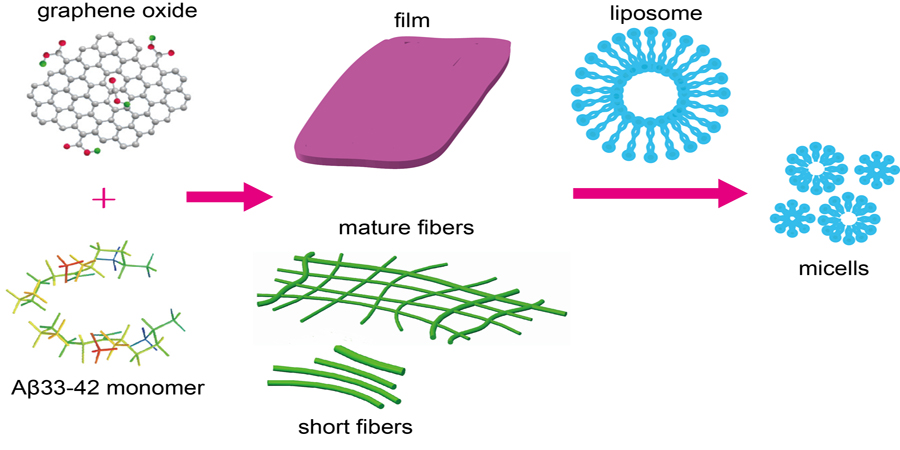
AFM study on amyloid peptide - graphene oxide assembly and its interaction with liposome
Abstract
The interaction between amyloid peptides and membrane is a broad
research topic due to the variety of biological events occurring, such as the membrane
disruption related pathogenesis of amyloid diseases or the toxicity of peptide
materials. Amyloid peptides have many structural forms, it is therefore important to
explore the interactions between the membrane and assemblies of amyloid peptides,
and to find ways to control these interactions. Herein, we utilized atomic force
microscopy (AFM) and circular dichroism spectra to explore the modulating effect of
Graphene Oxide (GO) on amyloid peptide assembly. In addition, the interaction
between liposome samples and amyloid peptide assembly modulated by GO was
investigated. It is achieved that the membrane disruption of amyloid peptide
aggregates can be fine-tuned by tweaking the GO concentration. The findings in this
work provide a better understanding of amyloid peptide and membrane interactions
and how it can be tuned.
Downloads
References
S. M. Butterfield and H. A. Lashuel, Amyloidogenic protein–membrane interactions:
mechanistic insight from model systems, Angewandte Chemie International Edition,
(33):5628-5654(2010).
G. G. Glenner, D. Ein, E. D. Eanes, H. A. Bladen, W. Terry and D. L. Page, Creation of
“amyloid” fibrils from Bence Jones proteins in vitro, Science, 174(4010):712-714 (1971).
G. G. Glenner, Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The β-fibrilloses, The New England Journal
of Medicine, 302(23), 1333-1343 (1980).
S. J. Soscia, J. E. Kirby, K. J. Washicosky, S. M. Tucker, M. Ingelsson, B. Hyman, M. A.
Burton, L.E. Goldstein, S.Duong, R. E. Tanzi and R. D. Moir, The Alzheimer's disease-associated
amyloid β-protein is an antimicrobial peptide, PlOS ONE, 5(3): e9505(2010).
E. D. Roberson and L. Mucke, 100 years and counting: prospects for defeating Alzheimer's
disease, Science, 314(5800): 781-784 (2006).
D. L. Brody, S. Magnoni, K. E. Schwetye, M. L. Spinner, T. J. Esparza, N. Stocchetti, G. J.
Zipfel and D. M. Holtzman, Amyloid-β dynamics correlate with neurological status in the injured
human brain, Science, 321(5893): 1221-1224 (2008).
E. Mikros, D. Benaki, E. Humpfer, M. Spraul, S. Loukas, C. I.Stassinopoulou and M.
Pelecanou, High-Resolution NMR Spectroscopy of the β‐Amyloid (1–28) Fibril Typical for
Alzheimer's Disease, Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 40(19):3603-3605(2001).
M. S. R. Shearman, C. I. Ragan and L. L. Iversen, Inhibition of PC12 cell redox activity is a
specific, early indicator of the mechanism of beta-amyloid-mediated cell death, Proc. Natl. Acad,
Sci. U.S.A., 91(4): 1470-1474(1994).
L. Liu, L. Zhang, L. Niu, M. Xu, X. B. Mao, Y. L. Yang and C.Wang, Observation of reduced
cytotoxicity of aggregated amyloidogenic peptides with chaperone-like molecules, ACS Nano,
(7): 6001-6007(2011).
J. Herms, C. Priller, T. Bauer, G. Mitteregger, B. Krebs and H. A.Kretzschmar, Synapse
formation and function is modulated by the amyloid precursor protein, Journal of Neuroscience,
(27): 7212-7221 (2006).
D. J. Selkoe, Physiological production of the β-amyloid protein and the mechanism of
Alzheimer's disease, Trends in Neurosciences, 16(10): 403-409 (1993).
L. Liu, L. Zhang, X. B. Mao, L. Niu, Y. L. Yang and C. Wang, Chaperon-mediated single
molecular approach toward modulating Aβ peptide aggregation, Nano Letters,
(12):4066-4072(2009).
M. Zhang, X. Mao, Y. Yu, C. X. Wang, Y. L. Yang and C. Wang, Nanomaterials for reducing
amyloid cytotoxicity, Advanced Materials, 25(28):3780-3801(2013).
C. Li and R. Mezzenga, The interplay between carbon nanomaterials and amyloid fibrils in
bio-nanotechnology,Nanoscale, 5(14): 6207-6218 (2013).
J. E. Kim and M. Lee, Fullerene inhibits β-amyloid peptide aggregation, Biochem. Biophys.
Res. Commun., 303(2):576-579(2003).
H. Li, Y. Luo, P. Derreumaux and G. Wei, Carbon nanotube inhibits the formation of
β-sheet-rich oligomers of the Alzheimer's amyloid-β (16-22) peptide, Biophysical Journal,
(9):2267-2276(2011).
Z. Fu, Y. Luo, P. Derreumaux and G. Wei, Induced β-Barrel Formation of the Alzheimer's
Aβ25–35 Oligomers on Carbon Nanotube Surfaces:Implication for Amyloid Fibril Inhibition,
Biophysical Journal, 97(6): 1795-1803(2009).
A. K. Jana and N. Sengupta, Adsorption Mechanism and Collapse Propensities of the
Full-Length, Monomeric Aβ 1-42 on the Surface of a Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube: A
Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study Biophysical Journal, 102(8): 1889-1896(2012).
A. K. Jana, J. C. Jose and N. Sengupta, Critical roles of key domains in complete adsorption
of Aβ peptide on single-walled carbon nanotubes: insights with point mutations and MD
simulations, Phys.Chem. Chem. Phys, 15(3): 837-844 (2013).
V. C. Sanchez, A. Jachak, R. H. Hurt and A. B.Kane, Biological interactions of
graphene-family nanomaterials: an interdisciplinary review, Chem. Res. Toxicol, 25(1):
-34(2011).
L. Feng and Z. Liu, Graphene in biomedicine: opportunities and challenges,
Nanomedicine ,6(2): 317-324(2011).
Z. Liu, J. T. Robinson, X. Sun and H. Dai, PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of
water-insoluble cancer drugs, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 130(33):
-10877(2008).
Y. Zhang, T. R. Nayak, H. Hong and W. Cai, Graphene: a versatile nanoplatform for
biomedical applications, Nanoscale, 4(13): 3833-3842(2012).
S. K. Lee, H. Kim, B. S. Shim, Graphene: an emerging material for biological tissue
engineering ,Carbon Letters, 14(2):63-75 (2013).
H. Wang, Q. Zhang, X. Chu, T. Chen, J. Ge and R. Yu, Graphene oxide–peptide conjugate as
an intracellular protease sensor for caspase-3 activation imaging in live cells, Angew.Chem. Int.
Ed. 50(31): 7065-7069 (2011).
J. Balapanuru, J.X. Yang, S.Xiao, Q. Bao, M. Jahan, L. Polavarapu, J. Wei, Q. H. Xu and K. P.
Loh, A Graphene Oxide–Organic Dye Ionic Complex with DNA‐Sensing and Optical‐Limiting
Properties ,Angewandte Chemie, 122(37): 6699-6703(2010).
C.H. Lu, H. H.Yang, C. L. Zhu, X. Chen and G.N. Chen, A graphene platform for sensing
biomolecules, Angewandte Chemie, 121(26): 4879-4881 (2009).
H. Jang, Y. K. Kim, H. M. Kwon, W. S. Yeo, D. E.Kim and D.H. Min, A Graphene-Based
Platform for the Assay of Duplex‐DNA Unwinding by Helicase, Angewandte Chemie, 122(33):
-5843(2010).
J. H.Jung, D. S. Cheon, F. Liu, K. B. Lee and T. S. Seo, A Graphene Oxide Based
Immuno-biosensor for Pathogen Detection, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 49(33):5708-5711(2010).
X. Wang, C. Wang, K. Qu, Y. Song, J.Ren, D. Miyoshi, N. Sugimoto and X. Qu, Ultrasensitive
and Selective Detection of a Prognostic Indicator in Early-Stage Cancer Using Graphene Oxide
and Carbon Nanotubes, Advanced Functional Materials, 20(22):3967-3971 (2010).
M. Zhang, B. C. Yin, X. F. Wang and B. C. Ye, Interaction of peptides with graphene oxide
and its application for real-time monitoring of protease activity, Chemical Communications,
(8):2399-2401 (2011).
K. S. Novoselov, V.I. Fal'ko, L. Colombo, P. R. Gellert, M. G. Schwab and K. Kim, A roadmap
for graphene, Nature, 490(7419): 192-200 (2012).
Y. Tu, M. Lv, P. Xiu, T. Huynh, M. Zhang, M. Castelli, Z. Liu, Q.Huang, C. Fan, H. Fang and
R. Zhou, Destructive extraction of phospholipids from Escherichia coli membranes by graphene
nanosheets, Nature nanotechnology, 8(8): 594-601 (2013).
Y. Li, H. Yuan, A. von dem Bussche, M. Creighton, R. H. Hurt, A. B.Kane and H. Gao,
Graphene microsheets enter cells through spontaneous membrane penetration at edge asperities
and corner sites, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(30): 12295-12300(2013).
T. Kowalewski and D. M. Holtzman, In situ atomic force microscopy study of Alzheimer’s
β-amyloid peptide on different substrates:New insights into mechanism of β-sheet formation,
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 96(7): 3688-3693(1999).
D. Losic, L. L. Martin, M. I. Aguilar and D. H. Small, β‐Amyloid fibril formation is
promoted by step edges of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, Peptide Science, 84(5):519-526
(2006).
R. Laghaei, N. Mousseau and G. Wei, Structure and thermodynamics of amylin dimer studied
by hamiltonian-temperature replica exchange molecular dynamics simulations, J. Phys. Chem. B,
(12): 3146-3154(2011).
X. Yu, Q. Wang, Y. Lin, J. Zhao, C. Zhao and J. Zheng, Structure, orientation, and surface
interaction of Alzheimer amyloid-β peptides on the graphite, Langmuir, 28(16): 6595-6605(2012).
M.Mahmoudi, O. Akhavan, M. Ghavami, F. Rezaee and S. M. A. Ghiasi, Graphene oxide
strongly inhibits amyloid beta fibrillation, Nanoscale, 4(23), 7322-7325 (2012).
P. Liu, S. Zhang, M. S .Chen, Q. Liu, C. Wang, Y. M. Li, F. Besenbacher and M. D. Dong,
Co-assembly of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP)/insulin, Chem Commun,
(2):191–193(2012).
J. Adamcik, J. M. Jung, J. Flakowski, Paolo De Los Rios, G. Dietler and R. Mezzenga,
Understanding amyloid aggregation by statistical analysis of atomic force microscopy images, Nat
Nanotechnol, 5(6):423–428(2010).
M. D. Dong, M. B. Hovgaard, S. L. Xu, D. E. Otzen and F. Besenbacher, AFM study of
glucagon fibrillation via oligomeric structures resulting in interwoven fibrils, Nanotechnology,
(16):4003–4009(2006).
Y.P. Yu, S. Zhang, Q. Liu, Y. M. Li, C. Wang, F. Besenbacher and M. D. Dong, 2D amyloid
aggregation of human islet amyloid polypeptide at the solid-liquid interface, Soft Matter,
(5):1616–1622(2012).
A. Quist, I. Doudevski, H. Lin, R. Azimova, D. Ng, B. Frangione, B. Kagan, J. Ghiso and R.
Lal, Amyloid ion channels: A common structural link for proteinmisfolding disease, Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA, 102(30):10427–10432(2005).
J.Adamcik, V. Castelletto, S. Bolisetty, I. W. Hamley and R. Mezzenga, Direct observation of
time-resolved polymorphic states in the self-assembly of end-capped heptapeptides, Angew Chem
Int Ed Engl, 50(24):5495–5498(2011).
Q. Li, L. Liu, S. Zhang, M. Xu, X. Q. Wang, C. Wang, F. Besenbacher and M. D. Dong*,
Modulating Aβ33–42 Peptide Assembly by Graphene Oxide, Chemistry-A European Journal,
(24): 7236-7240 (2014).
E. Hellstrand, B. Boland, D. M. Walsh and S. Linse, Amyloid β-protein aggregation produces
highly reproducible kinetic data and occurs by a two-phase process, ACS Chem.Neurosci., 1(1):
-18(2009)